RAFキナーゼ
(Rafキナーゼから転送)
RAFキナーゼ(英: RAF kinase)は、レトロウイルスのがん遺伝子と関連した3つのセリン/スレオニンキナーゼからなるファミリーである[11]。マウス肉腫ウイルス3611はRAFキナーゼ関連がん遺伝子を持ち、この遺伝子は線維肉腫の誘導を亢進させる。RAFという名称は Rapidly Accelerated Fibrosarcoma の頭文字をとったものである[12]。
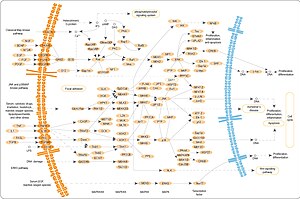
RAFキナーゼはRAS-RAF-MEK-ERKシグナル伝達カスケード(MAPK/ERK経路)に関与する[11]。RAFキナーゼの活性化にはRASとの相互作用が必要である。
RAFキナーゼファミリーは3つのメンバーから構成される。
出典
編集- ^ “Evidence that pp42, a major tyrosine kinase target protein, is a mitogen-activated serine/threonine protein kinase”. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 86 (18): 6940–3. (1989). doi:10.1073/pnas.86.18.6940. PMC 297966. PMID 2550926.
- ^ “Cell survival promoted by the Ras-MAPK signaling pathway by transcription-dependent and -independent mechanisms”. Science 286 (5443): 1358–62. (1999). doi:10.1126/science.286.5443.1358. PMID 10558990.
- ^ “Direct activation of mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase kinase MEKK1 by the Ste20p homologue GCK and the adapter protein TRAF2”. Mol. Cell. Biol. 22 (3): 737–49. (2002). doi:10.1128/MCB.22.3.737-749.2002. PMC 133545. PMID 11784851.
- ^ “Mammalian MAP kinase signaling cascades”. Nature 410 (6824): 37–40. (2001). doi:10.1038/35065000. PMID 11242034.
- ^ “The c-Jun N-terminal kinase pathway and apoptotic signaling (review)”. Int. J. Oncol. 16 (4): 651–62. (2000). doi:10.3892/ijo.16.4.651. PMID 10717232.
- ^ “MAPK-regulated transcription: a continuously variable gene switch?”. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 3 (1): 30–40. (2002). doi:10.1038/nrm715. PMID 11823796.
- ^ “BMK1/ERK5 regulates serum-induced early gene expression through transcription factor MEF2C”. EMBO J. 16 (23): 7054–66. (1997). doi:10.1093/emboj/16.23.7054. PMC 1170308. PMID 9384584.
- ^ “HPK1, a hematopoietic protein kinase activating the SAPK/JNK pathway”. EMBO J. 15 (24): 7013–25. (1996). doi:10.1002/j.1460-2075.1996.tb01093.x. PMC 452527. PMID 9003777.
- ^ “ERK5 and ERK2 cooperate to regulate NF-kappaB and cell transformation”. J. Biol. Chem. 276 (11): 7927–31. (2001). doi:10.1074/jbc.M009764200. PMC 4372717. PMID 11118448.
- ^ “Signal transduction. MAP kinase signaling specificity”. Science 296 (5577): 2345–7. (2002). doi:10.1126/science.1073344. PMID 12089430.
- ^ a b Roskoski R (August 2010). “RAF protein-serine/threonine kinases: structure and regulation”. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 399 (3): 313–7. doi:10.1016/j.bbrc.2010.07.092. PMID 20674547.
- ^ “Back to the roots: the remarkable RAF oncogene story”. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 63 (11): 1314–30. (June 2006). doi:10.1007/s00018-006-6005-y. PMID 16649144.