二形性真菌
二形性真菌(にけいせいしんきん、英語: Dimorphic fungus、二相性真菌とも呼ぶ)は、 一つの菌株が環境条件によって2つの異なる栄養増殖形態(カビ/菌糸/糸状菌型あるいは酵母型)を示す真菌である[1][2]。
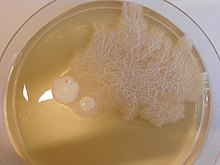
一例として、ヒト病原菌Penicillium marneffeiは室温ではカビとして、人間の体温では酵母として生育する[3]。
 仮性菌糸 |
|
| カンジダ・アルビカンス(Candida albicans) | |
|---|---|
出典
編集- ^ 鈴木 孝仁 (1995). “真菌の二形性とその調節”. Plant Morphol. 7 (1): 29–38. doi:10.5685/plmorphol.7.29.
- ^ “Fungi”. June 6, 2009時点のオリジナルよりアーカイブ。2009年6月6日閲覧。
- ^ Chandler JM, Treece ER, Trenary HR, et al. (2008). “Protein profiling of the dimorphic, pathogenic fungus, Penicillium marneffei”. Proteome Sci. 6 (1): 17. doi:10.1186/1477-5956-6-17. PMC 2478645. PMID 18533041.
