フッ化キュリウム(III)
フッ化キュリウム(III)(Curium(III) fluoride)は、キュリウムとフッ素からなる化学式CmF3の化合物である[3]。白色でほぼ不溶の塩であり、フッ化ランタン(III)と同じ結晶構造を持つ。
| フッ化キュリウム(III) | |
|---|---|
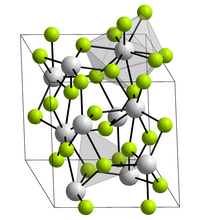 結晶構造
| |
Curium(III) fluoride | |
別称 Curium trifluoride | |
| 識別情報 | |
| CAS登録番号 | 13708-79-7 |
| PubChem | 101943145 |
| ChemSpider | 57569004 |
| |
| 特性 | |
| 化学式 | CmF3 |
| 外観 | 無色固体[1] |
| 融点 |
1406 ± 20 ℃; [1] |
| 水への溶解度 | ~10 mg/L |
| 構造 | |
| 結晶構造 | 菱面体, hR24 |
| 空間群 | P3c1, No. 165[2] |
| 格子定数 (a, b, c) | a = 0.7012 nm Å |
| 熱化学 | |
| 標準生成熱 ΔfH |
−1660 kJ/mol[1] |
| 標準モルエントロピー S |
121 J/mol·K[1] |
| 特記なき場合、データは常温 (25 °C)・常圧 (100 kPa) におけるものである。 | |
合成
編集弱酸性のCm(III)溶液にフッ化物イオンを添加すると、水和物として沈殿する。
または、フッ化水素酸と水酸化キュリウム(III)を反応させることでも合成できる[4]。その後乾燥させるか、フッ化水素ガスで処理すると無水物が得られる[1]。
出典
編集- ^ a b c d e Haire, Richard G. (2006). “Curium (9.7.3 Halides)”. In Morss; Edelstein, Norman M.; Fuger, Jean. The Chemistry of the Actinide and Transactinide Elements (3rd ed.). Dordrecht, The Netherlands: Springer Science+Business Media. p. 1417. doi:10.1007/1-4020-3598-5_9. ISBN 1-4020-3555-1
- ^ Nave, S. E.; Haire, R. G.; Huray, Paul G. (1983). “Magnetic properties of actinide elements having the 5f6 and 5f7 electronic configurations”. Physical Review B 28 (5): 2317. doi:10.1103/PhysRevB.28.2317.
- ^ Macintyre, Jane E. (23 July 1992) (英語). Dictionary of Inorganic Compounds. CRC Press. p. 3046. ISBN 978-0-412-30120-9 27 June 2023閲覧。
- ^ Lumetta, Gregg J.; Thompson, Major C.; Penneman, Robert A.; Eller, P. Gary (2006). Morss, Lester R.; Edelstein, Norman M.; Fuger, Jean. eds (英語). Curium. Dordrecht: Springer Netherlands. pp. 1397–1443. doi:10.1007/1-4020-3598-5_9. ISBN 978-1-4020-3598-2